Jun 20 2024
Chinese medicine team's latest study: Major breakthrough in TCM research on reducing diabetes risk
On June 3, 2024, the international authoritative medical journal JAMA Internal Medicine published a research result produced by YiLing Pharmaceuticals, with Prof. Jia Zhenhua of Hebei Institute of Integrative Medicine, Academician Tong Xiaolin and Prof. Lian Fengmei of Guang'anmen Hospital of China Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine as the co-corresponding authors.
The paper "Diabetes Prevention Effect of JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) on People with Abnormal Glucose Tolerance Combined with Multiple Metabolic Disorders - FOCUS Randomized Clinical Trial" reveals the effect of JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) granules in lowering glucose tolerance and preventing diabetes in people with abnormal glucose tolerance combined with multiple metabolic disorders through the intervention study of JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) on abnormal glucose tolerance in metabolic syndrome. The FOCUS Randomized Clinical Trial reveals the significant role of JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) granules in reducing the risk of diabetes in people with abnormal glucose tolerance and multiple metabolic disorders.
The paper noted that the study, which used a randomized, double-blind, placebo-parallel-controlled, multicenter design with the incidence of diabetes as the main evaluation index, was conducted from June 2019 to February 2023 in 21 cities and 35 hospitals in China, enrolling 889 cases of abnormal glucose tolerance combined with abdominal obesity aged 18-70 years old, accompanied by abnormalities of any index of metabolic Subjects with abnormalities in any of the indicators of metabolic syndrome were randomized in a 1:1 ratio, of which 885 were included in the full analysis set (442 in the JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) group and 443 in the placebo group). Subjects received standardized lifestyle interventions (including dietary modification, physical activity, etc.), and were orally administered JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) or placebo at a dose of 1 sachet/trip, 3 times/day, with a median follow-up time of up to 2.2 years.
Diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disease, continues to increase in prevalence globally and poses a significant challenge to public health systems. Abnormal glucose tolerance is understood to be an intermediate state between normal blood glucose levels and diabetes. The normal blood glucose level of human body is between 3.9-6.1mmol/L when fasting, and <7.8mmol/L two hours after meal. when there is fasting blood glucose ≥7.0mmol/L, or two hours after meal blood glucose ≥11.1mmol/L, or random blood glucose ≥11.1mmol/L, or glycated hemoglobin ≥6.5%, and accompanied by typical symptoms of diabetes. Diabetes mellitus is diagnosed when it is accompanied by typical diabetic symptoms. As a prediabetic state, people with abnormal glucose tolerance are also at significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The risk of diabetes is further increased when abnormal glucose tolerance is combined with other risk factors such as obesity, dyslipidemia and hypertension, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease by 34%. Therefore, effective interventions for people with abnormal glucose tolerance combined with multiple metabolic disorders are particularly important.
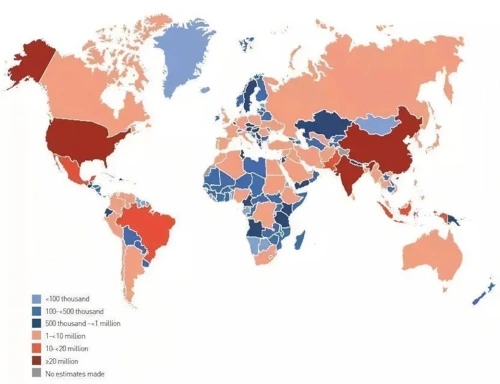
Global prevalence of diabetes as a percentage
This study is the first clinical evidence-based study led by a team of researchers in the field of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) to reduce the risk of diabetes in people with abnormal glucose tolerance combined with multiple metabolic disorders. The results of the study showed that the risk of diabetes was reduced by 41% in the JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) group compared to the placebo group. Meanwhile, several metabolic abnormalities, such as waist circumference, body mass index, fasting blood glucose, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and insulin resistance index were also significantly improved in the JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) group compared to the placebo group; and the key indexes of atherosclerosis, such as brachial and ankle indices and carotid intima-media thickness, were also significantly improved. The key indicators of atherosclerosis - arm and ankle index and carotid artery intima-media thickness - are also significantly different, indicating that JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) can reduce waist circumference and body mass index, regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, improve insulin resistance, and ameliorate multiple metabolic disorders to achieve the purpose of protecting blood vessels.
According to statistics, there is no evidence-based medical research that proves that pCms can reduce the risk of diabetes in people with abnormal glucose tolerance combined with multiple metabolic disorders. The publication of this research result proves that the clinical evidence-based medical trial that pCms can reduce the risk of diabetes in this population provides a more effective intervention for the prevention of diabetes, which is expected to help high-risk populations to reduce the risk of diabetes, thus reducing the burden of diabetes patients. In addition, as a traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation, JinLiDaKeLi (YiLing) Granules has proven its efficacy and safety in rigorous clinical trials, providing strong evidence for the modernization and internationalization of traditional Chinese medicine, and bringing new hope to hundreds of millions of high-risk diabetic people around the world.