Cold Brew vs. Hot Brew: Which Maximizes Healthy Tea Benefits?
When it comes to unlocking the full potential of Healthy Tea, the brewing method can make a significant difference. The age-old debate between cold brew and hot brew tea has left many tea enthusiasts wondering which approach truly maximizes the health benefits. Both methods have their merits, but the impact on nutrient content and overall wellness can vary. Let's delve into the world of tea brewing temperatures and uncover the secrets to harnessing the most potent health-boosting properties from your favorite herbal infusions.
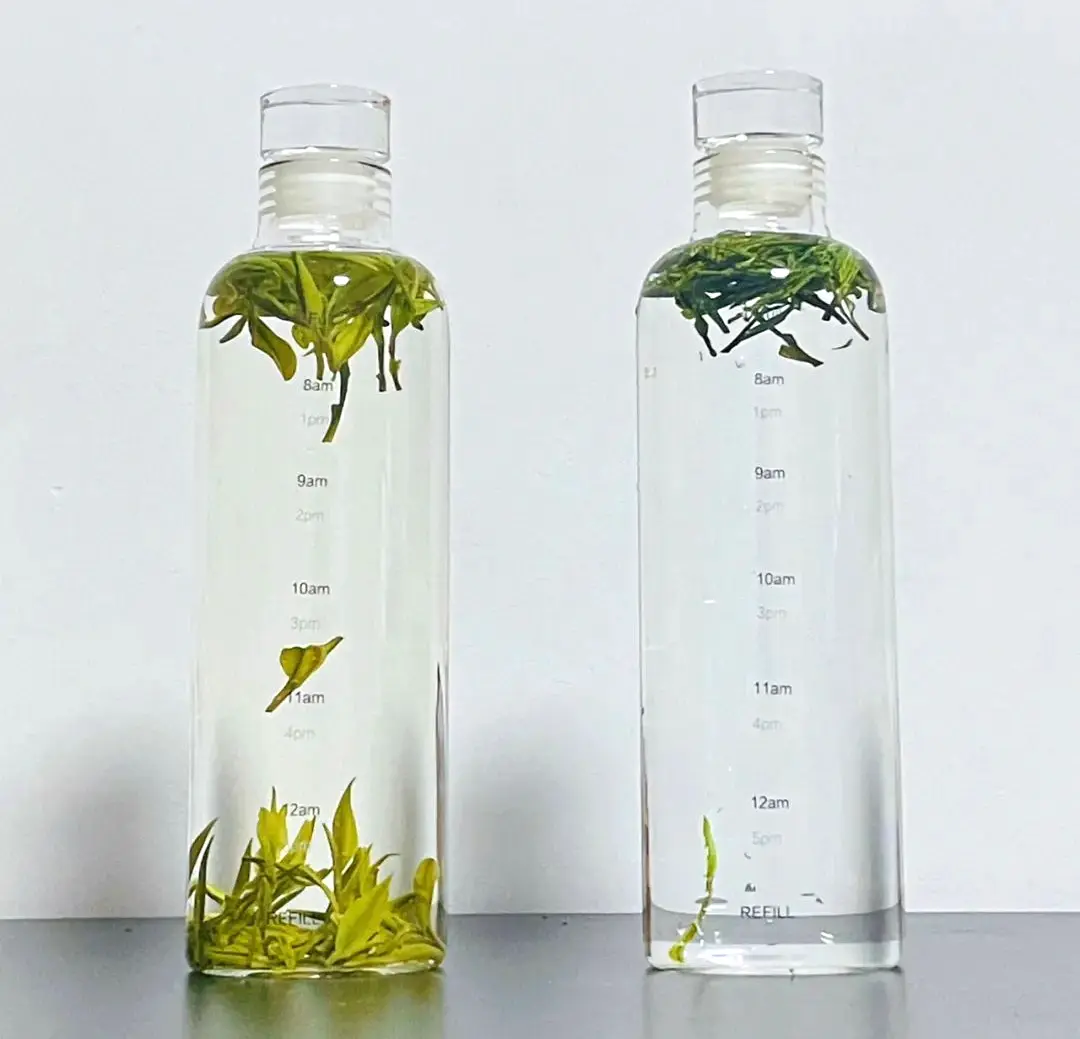

Table of Contents
How Does the Brewing Temperature Affect Tea's Nutrient Content?
The temperature at which tea is brewed plays a pivotal part in deciding the extraction of different compounds from tea clears out. Hot water tends to extricate more compounds rapidly, whereas cold water extraction is a slower handle that can surrender diverse results.
Hot Brewing: Fast Extraction of Compounds
When tea takes off are soaks in hot water, the warm causes the cell structures in the clears out to break down quickly. This speedy breakdown permits for the quick discharge of water-soluble compounds, counting caffeine, catechins, and other polyphenols. The higher temperature moreover encourages the extraction of unstable compounds that contribute to the healthy tea's smell and flavor profile.
Hot brewing is especially compelling at extricating certain sorts of cancer prevention agents, such as theaflavins and thearubigins, which are inexhaustible in dark teas. These compounds are known for their potential to back cardiovascular wellbeing and boost the safe framework. Moreover, hot water extraction tends to discharge more tannins, which contribute to the tea's astringent taste and may offer antimicrobial properties.
Cold Brewing: Tender Extraction and Preservation
Cold brewing, on the other hand, includes soaking tea clears out in cold or room temperature water for an amplified period, ordinarily a few hours or overnight. This moderate extraction handle comes about in a distinctive chemical profile compared to hot brewing. Cold water extraction is gentler on the tea clears out, which can lead to a smoother, less severe taste.
One of the preferences of cold brewing is that it may protect certain heat-sensitive compounds that seem be debased amid hot brewing. For illustration, a few thinks about propose that cold-brewed green tea may hold higher levels of catechins, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a powerful antioxidant related with different wellbeing benefits.
Cold brewing too tends to extricate less tannins, coming about in a less astringent taste. This can be especially useful for those who are delicate to the severity of hot-brewed teas or who encounter stomach related inconvenience from tannins.

What Are the Health Benefits of Cold Brew Tea Compared to Hot Brew?
Both cold and hot brew teas offer a range of health benefits, but there are some notable differences in their potential effects on well-being.
Antioxidant Content and Activity
Cold brew tea has been found to have a higher antioxidant activity compared to hot brew in some studies. This increased antioxidant potential may be due to the preservation of certain compounds that are sensitive to heat degradation. The gentle extraction process of cold brewing can result in a higher concentration of certain polyphenols and flavonoids, which are known for their ability to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
However, it's important to note that the antioxidant profile can vary depending on the type of healthy tea and specific brewing conditions. Some antioxidants may be more readily extracted in hot water, while others are better preserved through cold brewing.
Caffeine Content and Energy Boost
Cold brew tea typically contains less caffeine than its hot-brewed counterpart. This can be beneficial for those looking to reduce their caffeine intake or who are sensitive to its effects. The lower caffeine content in cold brew tea may provide a more gentle, sustained energy boost without the potential jitters or crash associated with higher caffeine levels.
For those seeking a stronger caffeine kick, hot-brewed tea may be more suitable. The higher temperature extraction process tends to release more caffeine from the tea leaves, resulting in a more stimulating beverage.
Digestive Health and Hydration
Cold brew tea may be easier on the digestive system for some individuals. The lower tannin content in cold-brewed tea can reduce the likelihood of stomach irritation or acid reflux that some people experience with hot-brewed teas. Additionally, the smoother, less bitter taste of cold brew tea may encourage increased fluid intake, promoting better hydration throughout the day.
On the other hand, hot-brewed tea has been traditionally valued for its potential to aid digestion, particularly when consumed after meals. The warmth of the beverage can help stimulate digestive processes and provide a soothing effect on the stomach.
Does Hot Brew Tea Retain More Antioxidants Than Cold Brew?
The question of whether hot brew tea retains more antioxidants than cold brew is complex and depends on various factors, including the type of tea, brewing time, and specific antioxidants in question.
Extraction Efficiency of Different Antioxidants
Hot brewing is generally more efficient at extracting certain types of antioxidants, particularly those that are more water-soluble at higher temperatures. For example, theaflavins and thearubigins, which are abundant in black teas, are more readily extracted in hot water. These compounds have been associated with potential cardiovascular benefits and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
However, cold brewing may be more effective at preserving certain heat-sensitive antioxidants, such as catechins found in green tea. Some studies have shown that cold-brewed green tea can retain higher levels of catechins, particularly EGCG, compared to hot-brewed green tea. EGCG is known for its potent antioxidant properties and has been linked to various health benefits, including potential anti-cancer and weight management effects.
Impact of Brewing Time on Antioxidant Levels
The duration of brewing also plays a role in antioxidant extraction. Hot brewing typically requires a shorter steeping time, usually ranging from 2 to 5 minutes, depending on the healthy tea type. This quick extraction can result in a high concentration of antioxidants in a relatively short period.
Cold brewing, on the other hand, involves a much longer steeping time, often 8 to 12 hours or more. This extended extraction period allows for a gradual release of compounds from the tea leaves, potentially resulting in a different antioxidant profile compared to hot-brewed tea.
Balancing Antioxidant Content and Bioavailability
While the total antioxidant content is important, it's also crucial to consider the bioavailability of these compounds. Bioavailability refers to the extent to which antioxidants can be absorbed and utilized by the body. Some studies suggest that the antioxidants in cold-brewed tea may have higher bioavailability compared to those in hot-brewed tea, potentially making them more effective in delivering health benefits.
It's worth noting that the impact of brewing temperature on antioxidant retention can vary significantly depending on the specific tea variety and the compounds of interest. For example, white teas and some herbal infusions may respond differently to hot and cold brewing methods compared to green or black teas.
Conclusion & Recommendations
In conclusion, the talk about between cold brew and hot brew tea in terms of maximizing wellbeing benefits is not a straightforward one. Both strategies have their merits, and the choice frequently depends on individual inclinations and particular wellbeing objectives. Cold brewing may offer preferences in terms of protecting certain heat-sensitive compounds and giving a smoother, less biting taste. On the other hand, hot brewing can be more proficient at extricating a wide extend of useful compounds quickly.
For those looking to tackle the full potential of healthy tea, consider joining both brewing strategies into your schedule. Test with distinctive tea assortments and brewing methods to discover the combination that best suits your taste inclinations and wellness destinations. Keep in mind that the quality of the tea clears out is fair as vital as the brewing strategy, so select high-quality, immaculate home grown teas for ideal wellbeing benefits.
If you're interested in investigating the world of premium home grown wellness teas, see no advance than Laicuherb. With over a century of skill in mixing Eastern intelligence with imaginative innovation, Laicuherb offers a extend of healthy tea choices outlined to meet the needs of health-conscious people. Whether you're a youthful proficient looking for characteristic ways to boost your well-being or a trade proprietor looking for to give your clients with top-quality home grown teas, Laicuherb has the culminate arrangement for you.
Experience the difference that pure, natural ingredients and advanced processing techniques can make in your tea-drinking journey. For more information on Laicuherb's products or to inquire about customization options, don't hesitate to reach out to us at hello@laicuherb.com. Discover the power of nature in every cup and take the first step towards a healthier, more balanced lifestyle with Laicuherb's expertly crafted herbal wellness teas.
References
- Journal of Food Science and Technology: "Comparison of antioxidant activity and bioactive compounds of tea infusions prepared by hot and cold brewing methods"
- Nutrients: "The Impact of Tea Processing Methods on the Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Tea"
- Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry: "Temperature and Time of Steeping Affect the Antioxidant Properties of White, Green, and Black Tea Infusions"
- Food Chemistry: "Influence of brewing method and temperature on the antioxidant capacity of green tea infusions"
- Molecular Nutrition & Food Research: "Bioavailability and Antioxidant Activity of Tea Flavanols after Consumption of Green Tea, Black Tea, or a Green Tea Extract Supplement"
- Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition: "Tea and Health: Studies in Humans"
About the Author
Laicuherb
The core content team at Laicuherb is a collective of experts, including health professionals, consultants in Traditional Chinese Medicine, and experienced content strategists. Some articles are authored by our brand's founders or R&D scientists. OLaicuherbur team has deep expertise in herbal health, integrating the wisdom of traditional medicine, modern nutrition, and women's health research to transform ancient wellness principles into practical, accessible content for everyday life.








